

- #Uuid generator v4 registration
- #Uuid generator v4 software
- #Uuid generator v4 code
- #Uuid generator v4 windows
Integer giving the low 32 bits of the time The canonical 8-4-4-4-12 format string is based on the record layout for the 16 bytes of the UUID: UUID record layout (See below.) In the example above, M is 1, and N is a (10xx 2), meaning that this is a version-1, variant-1 UUID that is, a time-based DCE/RFC 4122 UUID.
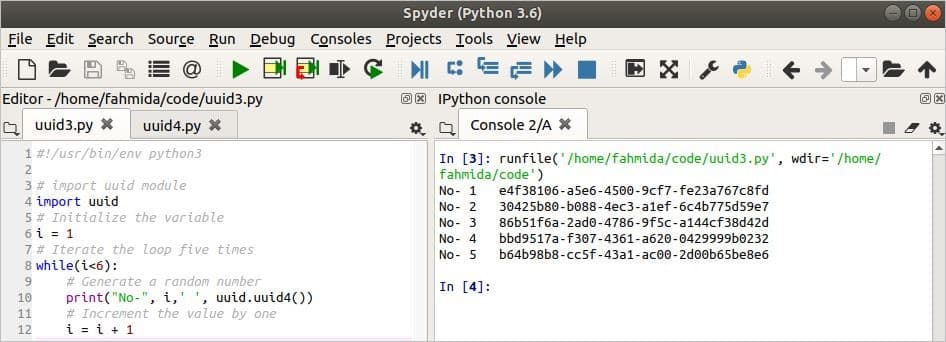
#Uuid generator v4 code
The four bits of digit M are the UUID version, and the 1 to 3 most significant bits of digit N code the UUID variant. The four-bit M and the 1- to 3-bit N fields code the format of the UUID itself. In its canonical textual representation, the 16 octets of a UUID are represented as 32 hexadecimal (base-16) digits, displayed in five groups separated by hyphens, in the form 8-4-4-4-12 for a total of 36 characters (32 hexadecimal characters and 4 hyphens). The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) published the Standards-Track RFC 4122, technically equivalent to ITU-T Rec. UUIDs are documented as part of ISO/ IEC 11578:1996 " Information technology – Open Systems Interconnection – Remote Procedure Call (RPC)" and more recently in ITU-T Rec.
#Uuid generator v4 software
UUIDs are standardized by the Open Software Foundation (OSF) as part of the Distributed Computing Environment (DCE). When in July 20 was published as a proposed IETF standard, the ITU had also standardized UUIDs, based on the previous standards and early versions of RFC 4122. RFC 4122 registered a URN namespace for UUIDs and recapitulated the earlier specifications, with the same technical content.
#Uuid generator v4 windows
Later, the Microsoft Windows platforms adopted the DCE design as "globally unique identifiers" (GUIDs). The initial design of DCE UUIDs was based on the NCS UUIDs, whose design was in turn inspired by the ( 64-bit) unique identifiers defined and used pervasively in Domain/OS, an operating system designed by Apollo Computer.
In the 1980s Apollo Computer originally used UUIDs in the Network Computing System (NCS) and later in the Open Software Foundation's (OSF) Distributed Computing Environment (DCE). Information labeled with UUIDs by independent parties can therefore be later combined into a single database or transmitted on the same channel, with a negligible probability of duplication.Īdoption of UUIDs is widespread, with many computing platforms providing support for generating them and for parsing their textual representation. Thus, anyone can create a UUID and use it to identify something with near certainty that the identifier does not duplicate one that has already been, or will be, created to identify something else. While the probability that a UUID will be duplicated is not zero, it is generally considered close enough to zero to be negligible.
#Uuid generator v4 registration
Their uniqueness does not depend on a central registration authority or coordination between the parties generating them, unlike most other numbering schemes. When generated according to the standard methods, UUIDs are, for practical purposes, unique. The term globally unique identifier ( GUID) is also used. Information labeled with UUIDs by independent parties can therefore be later combined into a single database, or transmitted on the same channel, without needing to resolve conflicts between identifiers.Īdoption of UUIDs and GUIDs is widespread, with many computing platforms providing support for generating them, and for parsing their textual representation.A universally unique identifier ( UUID) is a 128-bit label used for information in computer systems.

While the probability that a UUID will be duplicated is not zero, it is so close to zero as to be negligible. When generated according to the standard methods, UUIDs are for practical purposes unique, without depending for their uniqueness on a central registration authority or coordination between the parties generating them, unlike most other numbering schemes. The term globally unique identifier (GUID) is also used. Other UUID Versions UUID version 1 UUID version 3 UUID version 5Ī universally unique identifier (UUID) is a 128-bit number used to identify information in computer systems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
